Chemical composition and anticholinesterase evaluation of aerial parts of Crotalaria retusa
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.70151/3gfe1e75Keywords:
Crotalaria retusa, volatile constituents, acetylcholinesterase, chemical compositionAbstract
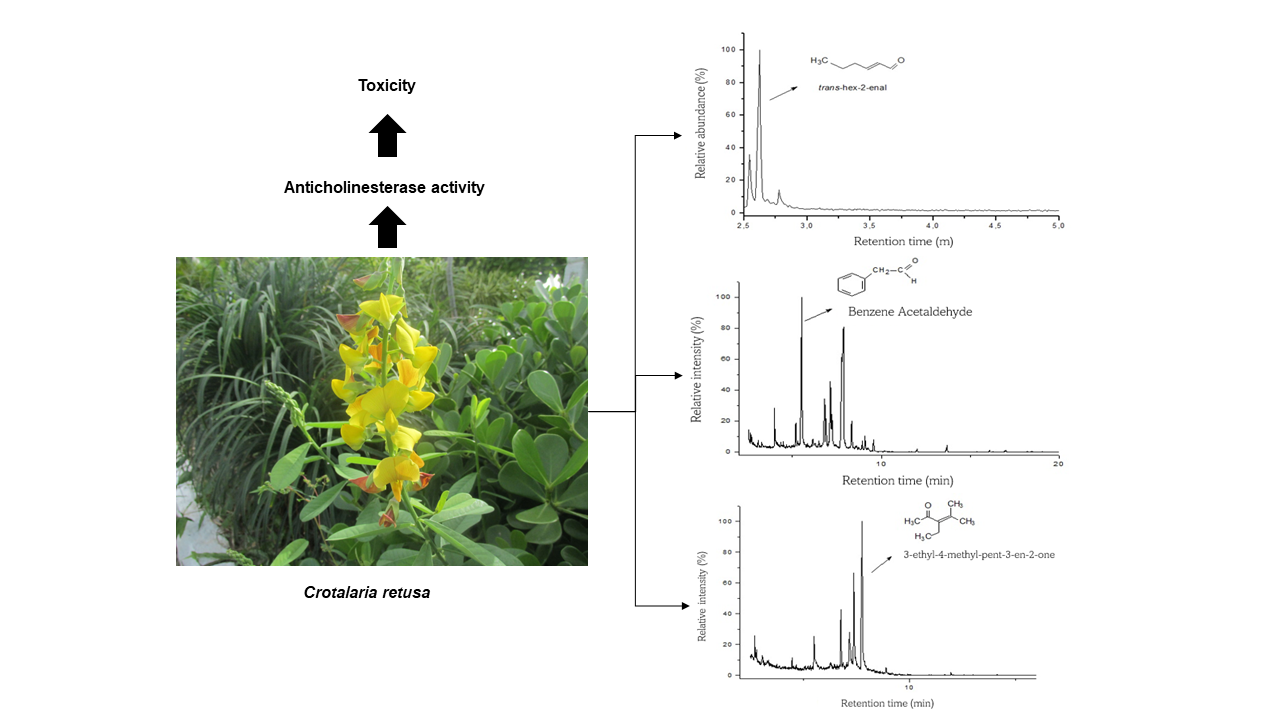
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibition is considered as a promising strategy for the treatment of neurological disorders. The aim of this research was to determine the chemical composition of the aerial parts of Crotalaria retusa by gas chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry (GC-MS), and evaluate their anticholinesterase and cytotoxic potential against Artemia salina. The main compounds found were trans-hex-2-enal (66.67%) in fresh leaves; in dry leaves benzene acetaldehyde (23.90%), and in fresh flowers 3-ethyl-4-methyl-pent-3-en-2-one (42.80%). The volatile constituents of fresh leaves, hexane and ethanolic extracts, decoction and dichloromethane fraction showed inhibition against AChE. The extracts were found to be nontoxic against Artemia salina, which increases the perspectives of study of the species about new biological activities.
Downloads
References
Adam RP (2007) Identification of essential oil components by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Allured publishing corporation Carol stream, llinois.
Ahmed F, Ghalib RM, Sasikala P, Ahmed KM (2013) Cholinesterase inhibitors from botanicals. Pharmacogn Rev 7(14):121–130. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-7847.120511
Ali MY, Jannat S, Jung HA, Choi RJ, Roy A, Choi JS (2016) Anti-Alzheimer's disease potential of coumarins from Angelica decursiva and Artemisia capillaris and structure-activity analysis. Asian Pac J Trop Med 9(2):103-111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apjtm.2016.01.014
Barbosa Filho JM, Medeiros KCP, Diniz MDFF, Batista LM, Athayde-Filho PF, Silva MS, da-Cunha EVL, Silva Almeida JRG, Quintans-Júnior LJ (2006) Natural products inhibitors of the enzyme acetylcholinesterase. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn 16(2):258-285. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0102-695X2006000200021
Charles DJ, Simon JE (1990) Comparison of extraction methods for the rapid determination of essential oil content and composition of basil. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 115(3):458-462. https://doi.org/10.21273/JASHS.115.3.458
Colovic MB, Krstic DZ, Lazarevic-Pasti TD, Bondzic AM, Vasic VM (2013) Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: pharmacology and toxicology. Curr Neuropharmacol 11(3):315-335. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X11311030006
da Silva FV, de Barros Fernandes H, Oliveira IS, Viana AFSC, da Costa DS, Lopes MTP, Oliveira RDCM (2016) Beta-cyclodextrin enhanced gastroprotective effect of (−)-linalool, a monoterpene present in rosewood essential oil, in gastric lesion models. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 389(11):1245-1251. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-016-1298-3
Dias CN, Rodrigues KA, Carvalho FA, Carneiro SM, Maia JG, Andrade EH, Moraes DF (2013) Molluscicidal and leishmanicidal activity of the leaf essential oil of Syzygium cumini (L.) Skeels from Brazil. Chem Biodivers 10(6):1133-1141. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbdv.201200292
Dohi S, Terasaki M, Makino M (2009) Acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity and chemical composition of commercial essential oils. J Agric Food Chem 57(10):4313-4318. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf804013j
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7(2):91-95. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-2952(61)90145-9
Feitosa CM, Freitas RM, Luz NNN, Bezerra MZB, Trevisan MTS (2011) Acetylcholinesterase inhibition by somes promising Brazilian medicinal plants. Braz J Biol 71(3):783-789. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1519-69842011000400025
Giordani RB, Pagliosa L, Henriques AT, Zuanazzi JAS, Dutilh JHA (2008) Antioxidant and anticolinesterasic effects of Hippeastrum species (Amaryllidaceae). Quím Nova 31(8):2042-2046. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-40422008000800024.
Gomes ADM, Koszuoski R (2005) Current evidence of the impact of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors on mild cognitive impairment and vascular dementia. Rev Psiquiatr Rio Gd Sul 27(2):197-205. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0101-81082005000200010
Hatanaka A, Harada T (1973) Formation of cis-3-hexenal, trans-2-hexenal and cis-3-hexenol in macerated Thea sinensis leaves. Phytochemistry 12(10):2341-2346. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-9422(73)80435-2
Hatanaka A, Kajiwara T, Sekiya J (1976) Biosynthesis of trans-2-hexenal in chloroplasts from Thea sinensis. Phytochemistry 15(7):1125-1126. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-9422(76)85114-X
Honório JER, Júnior Soares PM, Melo CL, Arruda Filho ACV, Sena Filho JG, Barbosa Filho JM, Sousa FCF, Fonteles MMF, Leal LKA, Queiroz MGR, Vasconcelos SMM (2010) Pharmacological activity of monocrotalina isolated from plants of the genus Crotalaria. Rev Bras Farmacogn 20(3):453-458. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0102-695X2010000300025
Ingkaninan K, Hazekamp A, Hoek AC, Balconi S, Verpoorte R (2000) Application of centrifugal partition chromatography in a general separation and dereplication procedure for plant extracts. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol 23(14):2195-2208. https://doi.org/10.1081/JLC-100100481
Ingkaninan K, Hermans-Lokkerbol ACJ, Verpoorte R (1999) Comparison of some centrifugal partition chromatography systems for a general separation of plant extracts. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol, 22(6):885-896. https://doi.org/10.1081/JLC-100101705
Kennedy DO, Dodd FL, Robertson BC, Okello EJ, Reay JL, Scholey AB, Haskell CF (2011) Monoterpenoid extract of sage (Salvia lavandulaefolia) with cholinesterase inhibiting properties improves cognitive performance and mood in healthy adults. J Psychopharmacol 25(8):1088-1100. https://doi.org/10.1177/0269881110385594
Kiendrebeogo M, Coulibaly AY, Nebie RC, Zeba B, Lamien CE, Lamien-Meda A, Nacoulma OG (2011) Antiacetylcholinesterase and antioxidant activity of essential oils from six medicinal plants from Burkina Faso. Rev Bras Farmacogn 21(1):63-69. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0102-695X2011005000008
Kumar GP, Khanum F (2012) Neuroprotective potential of phytochemicals. Pharmacogn Rev 6(12):81. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-7847.99898
Lucena RB, Rissi DR, Maia LA, Flores MM, Dantas AFM, Nobre VMD, Barros CS (2010) Poisoning by pyrrolizidine alkaloids in ruminants and horses in Brazil. Pesq Vet Bras 30(5):447-452. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-736X2010000500013
Mathew M, Subramanian S (2014) In vitro screening for anti-cholinesterase and antioxidant activity of methanolic extracts of Ayurvedic Medicinal Plants used for cognitive disorders. Plos One 9(1):86804. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0086804
Meyer BN, Ferrigni NR, Putnam JE, Jacobsen LB, Nichols DJ, Mclaughlin JL (1928) Brine shrimp: a convenient general bioassay for active plant constituents. Planta Med 45(5):31-34. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-971236
Mota WM, Barros ML, Cunha PEL, Santana MVA, Stevam CS, Leopoldo PTG, Fernandes RPM (2012) Evaluation of acetylcholinesterase inhibition by extracts from medicinal plants. Rev Bras Plantas Med 14(4):624-628. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-05722012000400008.
Mufson EJ, Counts SE, Perez SE, Ginsberg SD (2008) Cholinergic system during the progression of Alzheimer’s disease: therapeutic implications. Expert Rev Neurother 8(1):1703-1718. https://doi.org/10.1586/14737175.8.11.1703
Mukherjee PK, Kumar V, Mal M, Houghton PJ (2007) Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors from plants. Phytomedicine 14(4):289-300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2007.02.002
Murray AP, Faraoni MB, Castro MJ, Alza NP, Cavallaro V (2013) Natural AChE inhibitors from plants and their contribution to Alzheimer’s disease therapy. Curr Neuropharmacol 11(4):388-413. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X11311040004
Nobre VMT, Riet-Correa F, Filho JMB, Dantas AFM, Tabosa IM, Vasconcelos JS (2004) Poisoning by Crotalaria retusa (Fabaceae) in Equidae in the semiarid region of Paraíba. Pesq Vet Bras 24(3):132-143. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-736X2004000300004
Oboh G, Akinyemi AJ, Omojokun OS, Oyeleye IS (2014) Anticholinesterase and antioxidative properties of aqueous extract of Cola acuminata seed in vitro. Int J Alzheimers Dis. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/498629
Owokotomo IA, Ekundayo OE, Abayomi TG, Chukwuka AV (2015) In-vitro anti-cholinesterase activity of essential oil from four tropical medicinal plants. Toxicol Rep 2:850–857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2015.05.003
Peres JCF, Carvalho LRD, Gonçalez E, Berian LOS, Felicio JD (2012) Evaluation of antifungal activity of seaweed extracts. Ciênc. Agrotec 36(3):294-299. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1413-70542012000300004
Rhee IK, Van de Meent M, Ingkaninan K, Verpoorte R (2001) Screening for acetylcholinesterase inhibitors from Amaryllidaceae using silica gel thin-layer chromatography in combination with bioactivity staining. J Chromatogr A 915(1):217-223. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0021-9673(01)00624-0
Roex EW, Keijzers R, Van Gestel CA (2003) Acetylcholinesterase inhibition and increased food consumption rate in the zebrafish, Danio rerio, after chronic exposure to parathion. Aquat Toxicol 64(4):451-460. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0166-445x(03)00100-0
Sereniki A, Vital MABF (2008) Alzheimer's disease: pathophysiological and pharmacological features. Rev Psiquiatr Rio Gd Sul 30(1). https://doi.org/10.1590/S0101-81082008000200002
Sodré ACB, Luz JMQ, Haber LL, Marques MO, Rodrigues CR, Blank AF (2012) Organic and mineral fertilization and chemical composition of lemon balm (Melissa officinalis) essential oil. Rev Bras Farmacogn 22(1):40-44. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0102-695X2011005000186
Souza KS, Pohlit AM, Silva DD, Nunomura SM, de Oliveira KMT, Gomes EO, Portela CN, Tadei WP, Mouchrek Filho VE, Silva DD, Galhiane MS, Chierice GO (2007) Atividade biológica de extratos, hidrolatos e óleos vegetais de pau-rosa (Aniba duckei Kostermans) e quantificação do linalol no hidrolato de folhas. Rev Bras Pl Med 9(2):1-7.
Trevisan MTS, Macedo FVV, Van de Meent M, Rhee IK, Verpoorte R (2003) Seleção de plantas com atividade anticolinasterase para tratamento da doença de Alzheimer. Quím Nova 26(3):301-304. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-40422003000300002
Ustun O, Senol FS, Kurkcuoglu M, Orhan IE, Kartal M, Baser KHC (2012) Investigation on chemical composition, anticholinesterase and antioxidant activities of extracts and essential oils of Turkish Pinus species and pycnogenol. Ind Crops Prod 38:115-123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2012.01.016
Viegas Junior C, Bolzani VDS, Furlan M, Fraga CAM, Barreiro EJ (2004) Natural products as candidates for useful drugs in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Quim Nova 27(4):655-660. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-40422004000400021
Zhao Y, Zhao B (2013) Oxidative stress and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/316523
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.

